

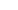




An electrical transformer is a crucial device used in the power distribution system. It is designed to change the voltage levels in electricity to facilitate long-distance transmission. In simple terms, a transformer helps ensure that electricity travels efficiently and effectively to homes and businesses. It operates based on the principle of electromagnetic induction, making it vital for any electrical circuit\'s stability.
Understanding how transformers work requires a focus on their key components and functions:
| Type | Function |
|---|---|
| Step Up Transformer | Increases voltage |
| Step Down Transformer | Decreases voltage |
| Isolation Transformer | Separates two circuits |
Electrical transformers are utilized in various applications globally:
Transformers offer several advantages, including:
In summary, electrical transformers play a vital role in ensuring efficient and safe power distribution worldwide. Understanding how they operate and their various types can greatly benefit manufacturers, distributors, and end-users alike when making informed decisions in the electrical industry. For global buyers and distributors, investing in quality transformers is a necessity for maintaining operational efficiency.
Oil Immersed Distribution Transformer VS Dry Type Cast Resin Transformer
In oil-immersed distribution transformers, oil is used as a heat conductor, and heat is released through radiator fins. Since the mineral oil has a flash point of 160 to 180°C, oil-immersed transformers must be installed in separate locations to prevent fire hazards in public spaces.
Aug. 25, 2025
Cast Resin Transformer: Definition, Types, Benefits, Applications, Maintenance
A cast resin dry-type transformer, also known as an epoxy cast resin dry-type transformer, is widely used due to its epoxy resin construction. Its windings are encased in high-quality protective material, ensuring robust insulation even in challenging environments with dust and humidity.
Aug. 22, 2025