

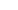




The cast resin transformer is a type of dry transformer that uses epoxy resin to encapsulate the windings and core, providing excellent insulation and environmental protection.
A cast resin dry-type transformer, also known as an epoxy cast resin dry-type transformer, is widely used due to its epoxy resin construction. Its windings are encased in high-quality protective material, ensuring robust insulation even in challenging environments with dust and humidity.
The resin casting process uses molds and specialized equipment to cast the coils under vacuum conditions. Epoxy resin, an insulating adhesive, makes the transformer non-flammable and suitable for indoor use.
The large heat capacity of the cast resin windings gives the transformer strong overload capacity and requires no maintenance, making it highly favored. With the growth of the global economy, demand for resin dry-type transformers is expected to increase rapidly.
Cast resin dry-type transformers operate on the principle of electromagnetic induction, similar to other transformers. When a conductive material is exposed to a varying magnetic field, an electric current is induced within the conductor.
AC voltage is applied to the primary winding of the transformer. As the AC current flows through the primary winding, it generates an alternating magnetic field, which is primarily confined within the iron or magnetic core. The secondary winding, wound around the same core, experiences this changing magnetic field, which induces an electromotive force (EMF) across its ends.
The voltage generated by the secondary winding differs from the input voltage while maintaining the same frequency and waveform as the input AC voltage.
Filled Resin Casting: Includes quartz powder to improve mechanical strength and thermal conductivity.
Unfilled Resin Casting: Uses pure epoxy resin without fillers, featuring a simpler construction.
Advantages:
Safe, fire-retardant, and suitable for indoor installation without special containment.
High electrical performance, resilient to short circuits, and requires minimal maintenance.
Energy-efficient and environmentally friendly.
Disadvantages:
Higher initial cost compared to oil-filled transformers.
Limited to lower voltage levels (up to 35kV) and capacities (up to 25,000 kVA).
Requires protection if used outdoors due to resin vulnerability to ultraviolet radiation and weather.
Oil-type transformers use mineral oil for insulation and cooling, while cast resin transformers use epoxy resin.
Oil-type transformers are versatile for both indoor and outdoor use, whereas cast resin transformers are predominantly used indoors.
Indoor Applications:
Ideal for areas with high fire safety requirements, such as shopping malls, hospitals, and high-rise buildings.
Outdoor Use:
Cast resin transformers can be used outdoors with proper weatherproof casing and protection against ultraviolet radiation.
Cast resin dry-type transformers generally require low maintenance but need periodic inspection for dust accumulation and insulation integrity.
Routine tests include insulation resistance, AC withstand voltage, and temperature monitoring to ensure safe and reliable operation.
Cast resin transformers provide significant advantages in safety, environmental friendliness, and reliability for indoor electrical distribution. Their use is essential in modern installations where fire safety and environmental considerations are prioritized, despite a higher initial cost compared to traditional oil-filled transformers.
Oil Immersed Distribution Transformer VS Dry Type Cast Resin Transformer
In oil-immersed distribution transformers, oil is used as a heat conductor, and heat is released through radiator fins. Since the mineral oil has a flash point of 160 to 180°C, oil-immersed transformers must be installed in separate locations to prevent fire hazards in public spaces.
Aug. 25, 2025
Cast Resin Transformer: Definition, Types, Benefits, Applications, Maintenance
A cast resin dry-type transformer, also known as an epoxy cast resin dry-type transformer, is widely used due to its epoxy resin construction. Its windings are encased in high-quality protective material, ensuring robust insulation even in challenging environments with dust and humidity.
Aug. 22, 2025